文章目录
本文将介绍区块链的工作原理,请reader带着如下几个问题进行阅读:
This paper will describe the working principles of the block chain & #xff0c; please read #xff1a with the following questions;
- 什么是区块链?
- 区块链是如何工作的?
- 如何确保区块链的安全性?
- 区块链可以应用在什么地方?
区块链是一个链式存储结构,区块就是链式存储结构中的数据元素,区块链由区块相互连接形成单向链式结构,其中第一个区块被称为创始区块。
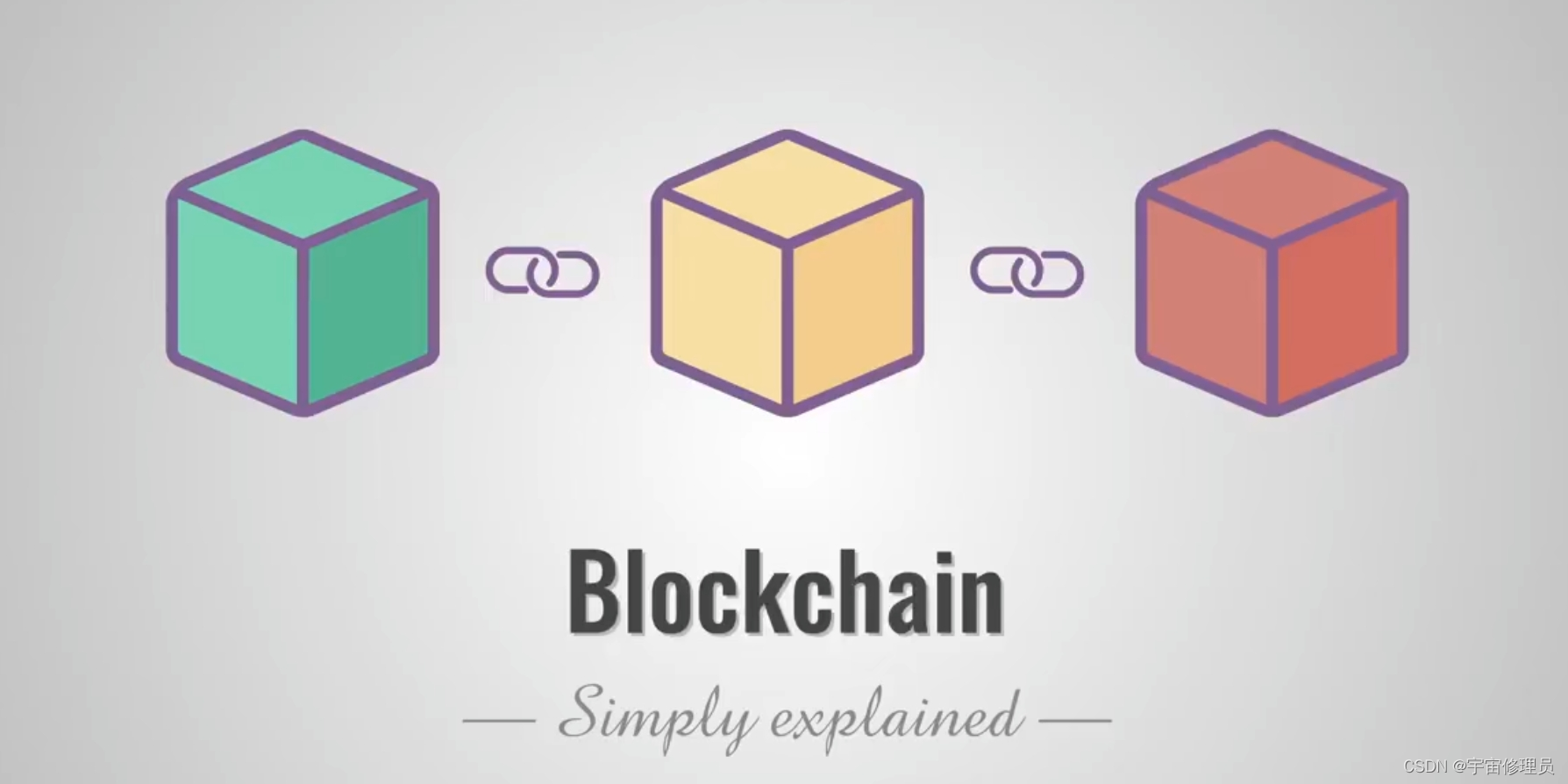
区块链的成长过程如下图。
The block chain is a chain storage structure xff0c; the block is the data element in the chain storage structure xff0c; the block chain is a one-way chain structure xff0c; the first of the blocks is called the original block.
 br/>
br/> 
区块链是一种分布式账本,对任何人都是开放的。
The block chain is a distributed account book xff0c; it is open to anyone.
分布式账本指的是交易记账由分布在不同地方的多个节点共同完成,而且每一个节点记录的是完整的账目,因此它们都可以参与监督交易合法性,同时也可以共同为其作证。
Distributed books refer to transactions where xff0c is performed jointly by multiple nodes distributed in different locations; and complete accounts xff0c are recorded in each node; they can therefore be involved in monitoring the legitimacy of the transaction xff0c; and they can be jointly testified to.
它们有一种有趣的性质:一旦数据被记录在区块链中,日后将很难被修改。这是如何做到的呢?我们首先了解一下区块的组成。
They have an interesting character xff1a; once the data is recorded in the block chain xff0c; it's hard to change later. How do you do that xff1f; let's start with the composition of the blocks.

每个数据块都含有三种元素。分别是:数据(Data)、Hash值、前一个区块的Hash值。

each data block contains three elements.
1.1数据(Data)
存储于块中的数据取决于块的类型。例如:比特币的区块链,记录了交易的细节。如发送人、接收者、钱币数量。

The data stored in a block depends on the type of block. For example, xff1a; Bitcoin's block chain xff0c; records details of the transaction.
1.2 Hash值
每个块本身有一个Hash值,该值是独一无二的,就好比每个人都有自己独一无二的指纹。它用于鉴定一个块和块的内容。当一个数据块被制作出来,它的Hash值同时也被计算出来了。
Each block itself has a Hash & #xff0c; it's a unique xff0c; it's like everyone has a unique fingerprint. It's used to identify the content of a block and a block. When a data block is made xff0c; its Hash value is also calculated.
如果想修改一个数据块的数据,就会同时改变其Hash值。换而言之,当你想检测数据库是否有变化时,Hash值就非常有用了。若一个数据块的Hash值发生了变动,那该块就不再是原来的自己。

If you want to change the data of a data block & #xff0c; you can change the Hash value at the same time. In other words, xff0c; xff0c; xff0c; xff0c; xff0c; b/ 
1.3 前一个区块的Hash值
该性质有效的建立了块与块之间的链接性,也正是这种性质保证了区块链的安全性。

This is a valid link between blocks and blocks & #xff0c; this is exactly what ensures the security of the block chain.

安全性保障经历了如下过程。
Security guarantees have gone through the following processes.

如下图,我们现在有一条包含三个块的区块链,可知每个块有一个独立的Hash值,和前一个块的Hash值。块3记录块2的Hash值,块2记录块1的Hash值。若黑客想篡改块2的Hash值,,则依次导致块3以及之后每一个块无效,因为它们不再存储前一个块有效的Hash值。
The following figure xff0c; we now have a block chain of three blocks xff0c; it is known that each block has an independent Hash value xff0c; and the previous Hash value. The Hash value of block 3 records the Hash value of block 2 xff0c; the Hash value of block 2 records the Hash value of block 1. If the hacker wants to change the Hash value of block 2 xff0c; xff0c; then each block of block 3 and each of the subsequent block becomes invalid xff0c; they no longer store the previous valid Hash value.
换言之,修改任意一个块的Hash值,都将导致后面所有块无效。由此,Hash值形成的链式结构使得区块链有一定的安全性。
In other words, xff0c; modifying the Hash value of xff0c of any one block; all of them will be invalid. The chain structure of this xff0c; Hash makes the block chain secure.
缺点:如今计算机的计算速度之快可以每秒计算成千上万个Hash值,若仅依靠哈希值是不足以防范篡改数据的问题的。

Deficiencies & #xff1a; computers can now calculate thousands of Hash & #xff0c values per second;

区块链共识机制的目标是使所有的诚实节点保存一致的区块链视图,同时满足两个性质:
1)一致性。所有诚实节点保存的区块链的前缀部分完全相同。
2)有效性。由某诚实节点发布的信息终将被其他所有诚实节点记录在自己的区块链中。
The goal of the block chain consensus mechanism is for all honest nodes to preserve a consistent block chain view xff0c; to satisfy both properties xff1a;
1xff09; consistency. All honest nodes save identical prefix parts of the block chain.
2xff09; validity. Information published by an honest node is eventually recorded in all other honest nodes in their block chain.
常见的共识就机制包括:POW(工作量证明机制)、POS(权益证明机制)、POW+POS(混合共识机制)、DPOS(股份授权证明)等。
Common consensus mechanisms include xff1a; POWxff08; workload certification mechanism xff09; POSff08; equity certification mechanism xff09; POW43; POSxff08; mixed consensus mechanism xff09; DPOSxff08; share authorization certificate xff09; etc.
此篇仅介绍其中一种共识机制:PoW(Proof of Work),即工作量证明技术。因为它需要比特币网络中的节点(矿工)以计算处理的形式进行某种类型的工作。
This article describes only one of the consensus mechanisms & #xff1a; PoW (Proof of Work) & #xff0c; i.e., workload proof technology. It requires nodes & #xff08 in the Bitcoin network; miners & #xff09; some type of work in the form of computational processing.
矿工是比特币网络的参与者,矿工需要检查和证明提交的交易的准确性。通常,费用最高的交易先进行。验证过程类似于解决一个非常复杂的数学问题。关于挖矿过程的另一个重要细节是难度调整。为了保持两个区块之间的时间不变,难度会在每 2016 个区块之后进行调整。通常,每 10 分钟(600 秒)就会发现一个新块。
The miners are the participants in the Bitcoin network xff0c; miners need to check and prove the accuracy of the transactions submitted. Usually xff0c; the most costly transactions are done first. The validation process is similar to solving a very complex mathematical problem. Another important detail about the mining process is the difficulty adjustment. To keep the time between the two blocks constant xff0c; the difficulty is adjusted after every 2016 block. Usually xff0c; every 10 minutes xff08; 600 seconds xff09; a new block is found.
当添加一个新块时,它还必须配备一个随机数(“数字仅使用一次”的缩写),用于进一步的加密目的。矿工改变随机数,直到找到一个值,使块的哈希具有所需的难度级别——一旦满足要求,就无法在不重新计算所有先前块的情况下更改块。
When a new block is added xff0c; it must also be equipped with a random number xff08; the acronym xff09; xff0c; used for further encryption purposes. Miners change the random number xff0c; until a value xff0c is found; to give Hash the level of difficulty required - once the requirements are met xff0c; cannot change the block without recalculating all previous blocks.
之后,节点对所选数据进行哈希处理,这基本上意味着数据被“切成小块”。在此过程中,散列函数(一种算法)转换选定的数据集并将其转换为固定大小的输出。该输出称为哈希值,用作原始值的掩码。
& xff0c; the node to process the selected data xff0c; this basically means that the data is " sliced into pieces ". In this process xff0c; hash function xff08; an algorithm xff09; the output to convert the selected data set to a fixed size. This output is called Hashi xff0c; it is used as a mask for the original value.
一个非常重要的事实是,哈希函数无法进行逆向工程——这意味着您无法从哈希值中找出原始数据。哈希值是一种指纹,确保一切都已正确完成。每个哈希值都包含有关所有先前进行的交易的信息。
A very important fact is that xff0c; the Hashi function cannot perform reverse work -- which means that you cannot find the original data from the Hashi value. The Hashi value is a fingerprint xff0c; ensure that everything is done correctly. Each Hashi value contains information about all previous transactions.
矿工生成许多具有不同随机数的散列,直到找到适合的散列。这个重复的过程被称为挖矿。当然,这需要大量的精力,因为 ASIC 矿工需要它来尝试许多不同的组合来找到合适的组合。然而,这就是比特币网络如此安全的原因。
The miners generate a lot of hash #xff0c with different random numbers; until a suitable hash is found. This repeat is called mining. Of course & #xff0c; this takes a lot of energy & #xff0c; because the ASIC miners need it to try many different combinations to find the right combination. However & #xff0c; that's why the Bitcoin network is so secure. 
参考博客:区块链之p2p网络
简单来说:人与人之间的纸质版合同形式换成程序的if-else语句执行。
Simplely & #xff1a; person-to-person paper-based form of contract executed in f-else.
举例来说:
#xff1a, for example;
智能合约是基于这些可信的不可篡改的数据,可以自动化的执行一些预先定义好的规则和条款。以保险为例,如果说每个人的信息(包括医疗信息和风险发生的信息)都是真实可信的,那就很容易的在一些标准化的保险产品中,去进行自动化的理赔。
——引用 百度百科Smart contracts are based on these credible and irrevocable data & #xff0c; some predefined rules and provisions can be automated. Insurance cases & #xff0c; if everyone's information & #xff08; including medical information and information about the occurrence of risk & #xff09; xff0c; easily automated claims in a number of standardized insurance products.
- quoted 100-degree encyclopedia


参考博文:区块链的应用领域
基于区块链的优点,结合应用领域中目前存在的隐患(缺点),进而推广区块链的使用。

Reference is made to the field of application of the block chain in Bovin & #xff1a;
based on the advantages of the block chain xff0c; in combination with the current pitfalls in the application area xff08; xff09; xff0c; and in further promoting the use of the block chain.

注册有任何问题请添加 微信:MVIP619 拉你进入群

打开微信扫一扫
添加客服
进入交流群


















发表评论